1. Introduction to a Healthy Lifestyle for a Healthy Heart
A Healthy Lifestyle For Healthy Heart is essential for maintaining a healthy heart and preventing heart disease, which is the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Unlike inherited influences, your lifestyle is under your control, making it the most effective tool for preserving excellent heart health. Small, persistent improvements in your daily habits can have long-term benefits for your heart and general health.
A Healthy Heart includes a balance of correct nutrition, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, efficient stress management, and avoiding from dangerous substances such as tobacco and excessive alcohol. These lifestyle decisions have an impact on key heart health elements such as blood pressure, cholesterol, weight, and blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, adopting Healthy Heart lowers the risk of developing illnesses such as hypertension, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol, all of which raise the risk of cardiovascular disease. The earlier you adopt heart-healthy practices, the better; however, it is never too late to begin.
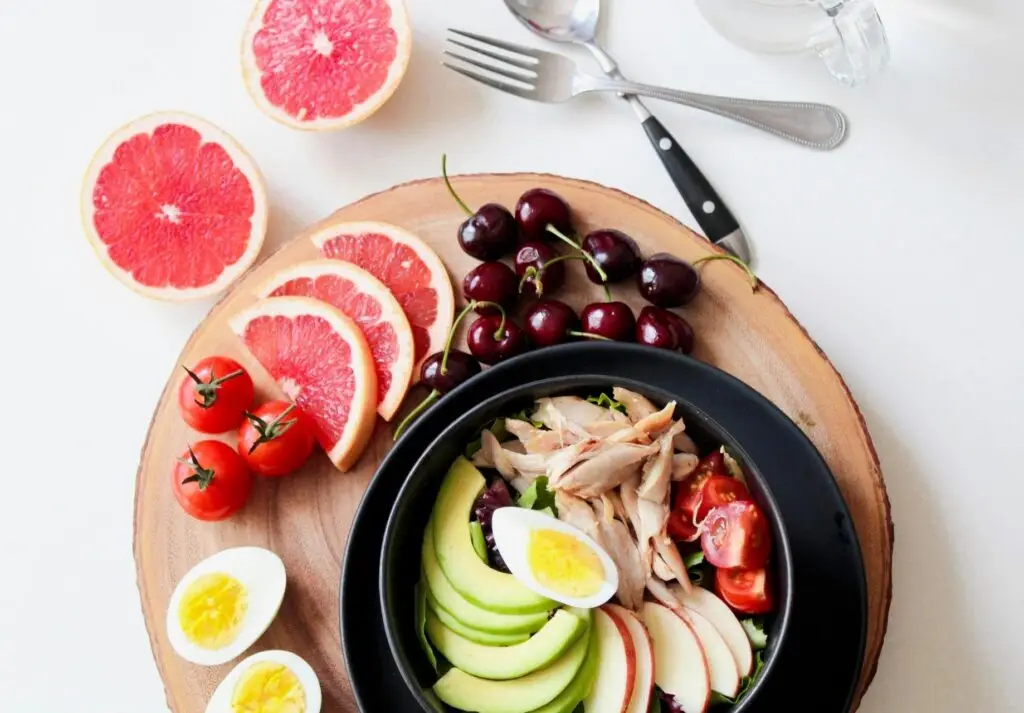

Table of Contents
2. Nutrition for a Healthy Lifestyle for a Healthy Heart
Eat a Balanced Diet
A well-balanced, nutrient-rich diet is essential for a healthy heart. What you eat on a daily basis has a direct impact on your cardiovascular health. A diet rich in heart-healthy foods can help lower blood pressure, cholesterol, maintain a healthy weight, and control blood sugar—all of which are necessary for cardiovascular health.
A Healthy Lifestyle For Healthy Heart begins with filling your plate with a variety of colorful fruits and veggies. These foods are high in antioxidants, fiber, and vitamins, all of which aid in the battle against inflammation and oxidative stress, two major causes to heart disease. Whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats are high in fiber and can help manage cholesterol levels.
Lean proteins, particularly seafood high in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon and sardines, help reduce inflammation and lower triglycerides. Plant-based proteins like beans, lentils, tofu, and almonds are also heart-healthy choices. Meanwhile, healthy fats like avocados, almonds, seeds, and olive oil should replace saturated and trans fats found in fried and processed foods and 5 ways to keep your heart healthy and happy
3. Physical Activity and Exercise
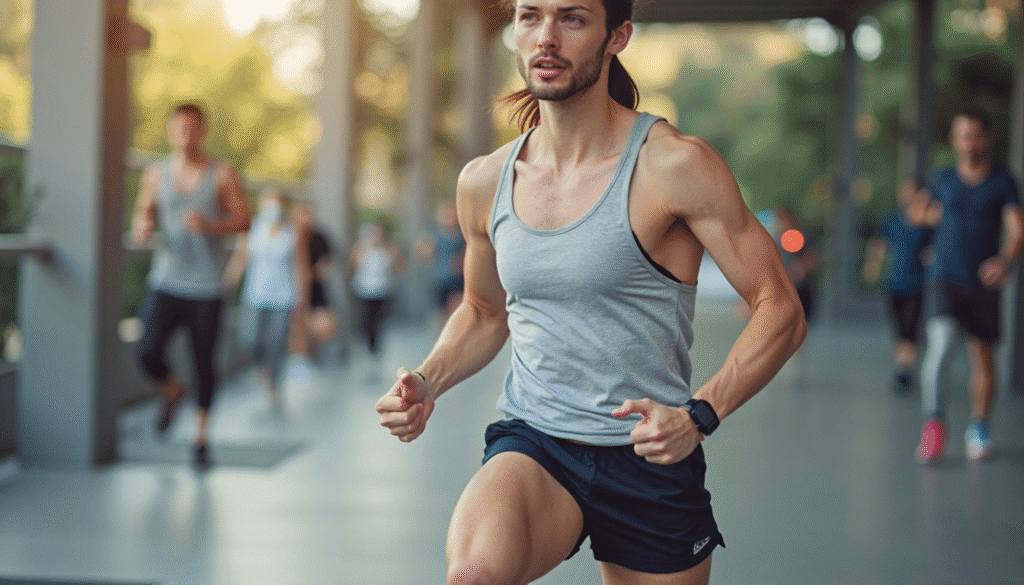

Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of A Healthy-Lifestyle For Healthy Heart. Exercise strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, lowers blood pressure, decreases bad cholesterol (LDL), boosts good cholesterol (HDL), and aids in blood sugar regulation. It also helps you maintain a healthy weight, which is important for preventing heart disease.
A. Make Physical Activity Part
Adding exercise to your daily routine does not have to be difficult. For a truly healthy-lifestyle, strive for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week e.g., brisk walking, dancing, or cycling or 75 minutes of intense activity. Aerobic exercises help your heart pump blood more efficiently.
B. Include Strength and Flexibility Training
Strength exercise two or more times per week is also advised as part of a healthy lifestyle for the heart. Lifting weights, utilizing resistance bands, and performing bodyweight workouts like push-ups and squats all contribute to the development of lean muscle mass, which aids metabolism and cardiovascular performance. Flexibility exercises, such as yoga or stretching, improve circulation and reduce injury risk, so supporting your active lifestyle.
C. Move More Throughout the Day
Living A Healthy-Lifestyle For Healthy Heart entails doing more than just exercise. Reduce sedentary time by standing, stretching, or walking every hour. Take stairs instead of elevators, park farther away from entrances, and consider walking meetings or active breaks. These brief spurts of exertion pile up and can make a significant difference in supporting your heart.
4. Weight Management for a Healthy Lifestyle for a Healthy Heart

Maintaining a healthy weight is an important component of living A Healthy Lifestyle For Healthy Heart. Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, raises the risk of significant cardiac problems such as hypertension, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, and coronary artery disease. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight improves circulation, minimizes stress on the heart, and keeps your cardiovascular system running smoothly.
A. Understand the Importance of Healthy Weight
Body Mass Index (BMI) and waist circumference are important indicators of heart health when combined with a healthy- lifestyle. A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is generally considered healthy, however a waist circumference more than 40 inches for men and 35 inches for women implies an increased risk of heart disease. However, rather than focusing solely on numbers on a scale, it is critical to consider your entire wellness and mood.
Weight loss does not have to be extreme to have a significant impact. Even decreasing 5% to 10% of your body weight can result in considerable improvements in blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and insulin sensitivity—all of which are critical components of a healthy-lifestyle for your heart.
B. Balance Calories to Support a Healthy Lifestyle
Weight control is based on balancing the calories you intake and the calories you burn. This entails eating nutrient-dense meals like whole grains, lean meats, fruits, healthy fast food and vegetables while avoiding high-calorie, low-nutrient options like sugary drinks, fast food, and high-fat snacks.
Physical activity is also important for maintaining this equilibrium. Regular exercise not only burns calories but also helps to maintain muscle mass while losing weight, which is critical for long-term success and metabolic health. Combining healthy eating habits with regular physical activity provides a solid basis for A Healthy Lifestyle For Healthy Heart.
V. Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol
Avoiding tobacco and restricting alcohol are two of the most effective ways to promote a healthy heart. Both smoking and binge drinking are important risk factors for heart disease, stroke, and other chronic health problems. Eliminating these hazardous habits will significantly enhance your heart health and overall well-being.
A. Quit Smoking to Strengthen Your Healthy Lifestyle
Smoking is one of the most harmful practices for heart health. It adds to plaque accumulation in the arteries (atherosclerosis), elevates blood pressure, lowers oxygen levels in the blood, and increases the chance of blood clots, all of which can lead to a heart attack or stroke. Even secondhand smoke poses severe cardiovascular hazards.
Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to live a healthy-lifestyle and protect your heart. The benefits start almost immediately—within 20 minutes, your heart rate reduces; within weeks, your circulation improves; and within a year, your risk of heart disease is reduced by half. You can successfully quit using support groups, nicotine replacement therapy, counseling, and apps.
B. Drink Alcohol in Moderation as Part of a Healthy Lifestyle
While some research suggest that moderate alcohol consumption may have some cardiovascular benefits, excessive drinking can have the opposite impact. It can increase blood pressure, contribute to high triglyceride levels, and cause irregular heart beats. Heavy alcohol consumption has also been linked to obesity and liver impairment, both of which put additional strain on your heart.
As part of a healthy lifestyle, women should restrict their alcohol intake to one drink per day and males to two drinks per day. If you don’t drink, there’s no reason to start—heart advantages can be obtained more safely through diet, exercise, and stress management.
6. Stress Management
Effective stress management is an essential component of a heart-healthy-lifestyle. While some stress is normal in life, prolonged stress might harm your cardiovascular health. It raises blood pressure, increases heart rate, and promotes inflammation, all of which stress the heart and increase the risk of heart disease over time.
A. Understand the Impact of Stress
When you’re stressed, your body creates hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. While these compounds are useful in an emergency, prolonged exposure to them can cause long-term damage, particularly if stress is not treated. Chronic stress can also lead to harmful coping behaviors like emotional eating, smoking, drinking alcohol, or avoiding physical activity, all of which are detrimental to a healthy-lifestyle.
Regular stress management practices are vital for preserving emotional balance and heart health. Mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation are all effective techniques to reduce stress and promote a healthy-lifestyle for the heart. Even spending time outside or engaging in activities can lower cortisol levels and enhance mood.
B. Sleep and Social Support
Adequate sleep is frequently disregarded, yet it is critical to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and a healthy heart. Poor sleep quality or insufficient rest raises the risk of high blood pressure, obesity, and irregular heartbeats. Aim for 7-9 hours of restorative sleep per night and create a consistent sleep schedule.
Strong social relationships also provide protection. Positive relationships help to reduce stress, increase mood, and offer emotional support during difficult times. Maintaining strong interpersonal relationships, whether with family, friends, or support groups, improves your capacity to live a healthy lifestyle.
Managing stress entails knowing how to deal with it in a healthy, constructive manner rather than fully eliminating it. Self-care, resilience, and finding quiet in everyday routines protect your heart and provide a solid basis for long-term wellness.
7. Regular Health Screenings
Managing stress includes understanding how to cope with it in a healthy, constructive way rather than completely removing it. Self-care, resilience, and finding peace in regular routines all benefit your heart and create a stable foundation for long-term wellness.
A. Monitor Blood Pressure and Cholesterol in a Healthy Lifestyle
High blood pressure (hypertension) is dubbed the “silent killer” because it can harm your heart and arteries without causing any visible symptoms. Regular blood pressure tests help keep your levels within a healthy range. A typical reading is normally less than 120/80 mmHg. If it is regularly higher, your doctor may suggest lifestyle modifications, drugs, or a combination of the two to control it.
Similarly, monitoring your cholesterol levels, particularly LDL (bad cholesterol), HDL (good cholesterol), and triglycerides, is critical for maintaining a healthy heart. High LDL levels can cause plaque accumulation in arteries, raising the risk of heart attack and stroke. Regular testing allows you to make the necessary dietary and lifestyle changes to keep your heart healthy.
B. Screen for Diabetes and Heart Risk Factors
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels caused by diabetes or prediabetes dramatically raise the risk of heart disease. That is why blood glucose testing is an essential component of your health-care routine. If you have a family history of diabetes, obesity, or a sedentary lifestyle, your doctor may prescribe screening even if you are under the age of 45.
For those who have already been diagnosed with chronic diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, or high cholesterol, regular follow-up visits are essential for effectively treating them as part of a healthy lifestyle. Medication adherence, weekly lab work, and regular physical exams all contribute to a more individualized and preventative approach to heart treatment.
C. Know Your Numbers and Stay Informed
Living A Healthy Lifestyle For Healthy Heart entails staying aware about your own health measurements. Know your blood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugar, weight, and waist circumference. Keeping track of these figures enables you to make better decisions and create more achievable goals.
8. Consistency and Habit Formation
Building and maintaining A Healthy Lifestyle For Healthy Heart is more than just short-term remedies or diets; it’s about developing consistent, long-term habits that benefit your heart health. When beneficial activities become ingrained in your daily practice, true change occurs. Consistency is the key to transforming effort into long-term outcomes.
A. Start Small and Be Consistent with Your Healthy Lifestyle
One of the most effective methods to start a healthy lifestyle is to make tiny, attainable adjustments. Instead of changing your entire routine at once, pick one or two habits to work on each week. For example, commit to walking 30 minutes each day, drinking water instead of soda, or cooking more meals at home. These minor changes are easier to maintain and eventually lead to big improvements in your heart health.
Over time, these behaviors become second nature. This continuous advancement generates momentum, promotes confidence, and prevents burnout. A Healthy Lifestyle For Healthy Heart does not require perfection; rather, it requires persistence and making better choices the majority of the time.
B. Set Realistic Goals and Track Progress in Your Healthy Lifestyle
Setting realistic, defined goals is an important step toward developing long-term habits. Instead of saying “I’ll eat better,” make a specific goal, such as “I’ll eat five servings of vegetables per day.” Track your progress with notebooks, apps, or simple checklists. This keeps you motivated and helps you uncover patterns or barriers that require attention.
Additionally, celebrate small victories. Every time you choose a healthy meal, take the stairs, or skip smoking, you’re reinforcing your commitment to a healthy lifestyle for a healthy heart. Positive reinforcement makes it easier to stay on track.
C. Make It a Lifestyle, Not a Phase
The term “lifestyle” refers to something that is continual rather than transient. Avoid crash diets, strenuous exercise regimens, and unsustainable health trends. Instead, create a regimen that reflects your personality, schedule, and interests. This could include choosing a fun kind of exercise, making simple nutritional meals, or developing a bedtime routine to ensure proper sleep.


Pingback: Lower Stomach Fat Workouts:10 Best Exercises -
Pingback: Sore Lower Back: Top 7 Reasons for the Pain -